Google updates: what they are and how to recover lost rankings
They are among the most anticipated, feared and discussed events in the world of digital marketing and SEO: Google Core Updates, Google’s updates, are significant and far-reaching changes that intervene in Google’s search algorithms and systems, released periodically throughout the year and usually announced officially so that site owners, content producers and SEOs have the right information to understand any changes that are noticed in terms of ranking and traffic. Born out of the need to keep the world’s leading search engine on the cutting edge, Google updates introduce changes that can rearrange the game, drastically affecting traffic and page visibility. For this reason, understanding what Google’s major updates are and how to deal with them is critical to staying competitive and not undoing all the work you’ve done.
What are Google Updates
A Google Update is an intervention that affects Google’s mythical algorithm, introducing changes that can represent a profound restructuring of the parameters by which it evaluates the quality and relevance of content.
Therefore, it is never just an update, but a moment that is of decisive importance in digital marketing because it can challenge established SEO techniques and longstanding approaches.
The concept of an “update” may seem almost trivial, but when it comes to Google it is anything but a mere technical improvement because it has tangible, often immediate, consequences for the operation and profitability of a website. All it takes is a small change in algorithm ranking criteria to redefine the entire landscape of search results, affecting not only page rankings but also the business strategies of companies that rely on organic traffic to attract visitors, customers and leads.
What are Google’s broad core updates
This is especially true of broad core updates, periodic interventions that are released at certain times of the year, usually every four months.
A broad core update or core update is a change to the search engine’s core algorithm, or the core (core) that makes Google’s “core” systems and, on a general level, search ranking work.
Defining a Google Core Update therefore means getting into the depths of the process by which Google refines its ability to find and propose high-quality results. In simpler terms, a Google Core Update is a substantial update to the search engine’s algorithm-that behind-the-scenes engine that analyzes myriad pages and decides, in fractions of a second, their placement within the search results pages.
The significance of Google updates
Not a day goes by, really, without Google releasing one or more changes with the aim of improving the quality of search results: most of these interventions are not particularly visible to users, but serve precisely to incrementally refine the search engine’s efficiency. Just to rattle off some numbers, in 2022 there were 4725 launches, 13,280 experiments with real-time traffic, 894,660 search quality tests, and 72,367 side-by-side experiments, as explained in the guide to how Google Search works.
Unlike minor updates, which may address individual aspects of the algorithm, a Core Update is comparable to a systemic overhaul: it involves a multitude of interconnected changes that often redefine how the search engine understands and evaluates complex concepts such as relevance, authority, creativity, and user expectations.
Indeed, as we have said elsewhere, Google’s core algorithm is actually a collection of algorithms that interpret signals from Web pages, with the goal of ranking the content that best responds to a search query. We know virtually nothing about Google’s secret formula for ranking and have vague news about the 200 factors used for ranking or some more specific algorithms, but from what (little) has been explained to us by Google we can say that the broad core updates affect the whole complex of this system.
Technically speaking, then, broad core updates are “substantial improvements to Google’s overall ranking processes,” are repeated several times a year, and are designed to increase the overall relevance of search results so that they are even more useful for everyone. They are broad, i.e., broad, because they do not target anything specific, but are designed to improve Google’s systems in general, and they apply simultaneously to all languages and versions of Google, because their implementation is global and simultaneous worldwide.
More specifically, the main algorithm updates are changes made to improve Search in general and “keep up with the changing nature of the Web,” and are designed to ensure that, overall, the search engine always presents relevant and authoritative content to users who search, and can also affect Google Discover.
What Google’s updates are for
It is not simply a matter of refining some technical detail; Core Updates are designed to address fundamental and sometimes emerging issues in the quality of search results. For example, more weight might be given to quality content in an update, or a new ability for the algorithm to understand more complex contexts, such as user search intent or local and global trends, might be introduced.
A Google Core Update rethinks, in a broad sense, the criteria behind the selection and ranking of results, recalibrating the importance of the factors involved. And because these updates can include rapid and innovative changes, their impact on search results tends to be drastic.
It’s like being on a roller coaster. Imagine we have been working for months or even years to optimize every aspect of a site, from keywords to internal link structure, from URL optimization to title management. Then, all of a sudden, after the release of a new Core Update, traffic drops dramatically. This drop is not accidental, nor is it the result of a strange unforeseen event: it is the result of a change in the power relations governing online visibility, of a shift in the rules of the game for anyone involved in the digital world.
The implications can vary from site to site: some pages may see an increase in traffic, while others may experience considerable declines. This volatility in SERPs resulting from a Core Update is dictated by the fact that Google is trying to improve its ability to deliver the best possible results. Our task, both as website managers and as SEO professionals, is to understand not only what this update means, but also how to adapt our strategies to continue to achieve favorable results by responding proactively and quickly to the constant changes in the online search world.
In this sense, the term “update” ends up being almost reductive: we are faced with structural changes that redefine the pattern through which sites gain (or lose) relevance and visibility online.
Why does Google release Core Updates?
Leaving aside the business aspects, Google has a well-defined mission: to organize global information and make it universally accessible and useful. But the digital world is evolving rapidly, and the continued growth of content on the web, the diversification of user queries, and the arrival of new technologies demand an increasingly sophisticated search mechanism.
Key algorithm updates, therefore, serve to maintain a high quality of the results offered to users, ensuring that content occupying the top positions in SERPs is relevant, authoritative, and responds accurately to search queries.
Every day, billions of searches are conducted by users around the world, who rely on the search engine to deliver increasingly accurate, relevant, and timely results. However, with the exponential expansion of information available online, it is not enough to take a static approach: user needs evolve, new trends emerge, and new types of content see the light of day. For this reason, Google periodically implements broad core updates, with the aim of improving the algorithm that governs the ranking of search results.
Improving the relevance of search results is the focus of Google’s efforts, and to achieve this, the company must constantly refine the criteria by which it evaluates and sorts content on the Web. With each Google core update, the algorithm is “trained” not only to recognize and understand new requirements, but also to prioritize content that better meets the most up-to-date quality criteria. More attention is then placed on aspects such as authority, reliability, content accuracy, user experience, and relevance to search intent.
Google acts not only with the purpose of improving the individual user’s experience, but also to consolidate the trust that users place in the search engine. If users began to perceive that the results provided lacked quality, reliability or relevance, the very value of the entire Google ecosystem would be undermined. Therefore, core updates become essential not only to keep up with evolving user expectations, but also to anticipate them, confirming Google’s position as the world’s most trusted and used search engine.
Transparency is another pillar of the goals Google pursues through core updates. Although each update is not revealed in great detail, the company increasingly tends to clearly communicate when an intervention has been launched, allowing webmasters, SEOs, and web developers to analyze the changes and make the necessary adjustments. This approach reinforces trust between Google and web practitioners, making it clear that, even in their sometimes challenging implications, these updates serve a larger purpose: to maintain the search engine’s credibility, for the benefit of all.
A practical example, the ranking of the best movies
Google’s guide also gives us some examples to understand how a major update works.
“We did in 2015 a list of the 100 best movies ever made” and now, in 2024, we want to update it. Of course, there will be changes, because “some new and wonderful films that never existed before will now be candidates for inclusion, or we may even re-evaluate some films and realize that they deserved a higher place on the list than before.” Thus, the ranking will change and films that were previously at the top and move down have not become “bad” or done anything wrong-there are “simply other films deserving of a higher place than their own.”
Similarly, if we write a food recommendation guide, such as a list of 20 favorite restaurants in a specific city, things can change quickly from when we initially wrote it. Some new restaurants that did not exist before are now candidates for the list; we may reevaluate some restaurants and realize that they move to a higher position on the list, given the number of consistently positive experiences we have had there, or to account for the need to reward restaurants that accept dogs. The list will change, and restaurants that move down are not necessarily “bad”; there are just more restaurants that make it into our top 20.
The continuous improvement of the algorithm
One of Google’s greatest strengths is precisely its ability to continually adapt and refine itself through a series of algorithmic improvements that, over time, have revolutionized the way the search engine understands users’ queries and offers them answers. Each time Google releases a core update, we are faced with another step forward in the algorithm’s optimization journey.
Google’s algorithm is not a static and final entity, but is designed to evolve and respond to the needs of a digital environment that changes daily. Refining the algorithm means that with each update, Google introduces new variables or modifies existing ones, with the intent of making the search engine increasingly capable of understanding the intent behind a query, including context and semantic nuances. For example, some updates allow Google to interpret longer, more conversational queries, while others place emphasis on identifying and enhancing content that addresses specific reader needs, such as verifiability, authoritativeness, and topic coverage spectrum.
The refinement of the algorithm affects not only the textual content presented in searches, but also other elements such as the technical quality of the website, the browsing experience offered to the user, and compatibility with mobile devices. Each Google update, therefore, represents a strategic action designed to reconfigure the SERP mapping and propose increasingly comprehensive and appropriate results to surfers. In essence, with each update, the algorithm becomes increasingly “smarter” and better equipped to respond to the changing demands of users seeking information in new and diverse ways.
Being aware that this refinement process is continuous and necessary allows us to frame core updates not as isolated and unpredictable episodes, but rather as moments in a process of constant improvement aimed at maintaining the relevance and topicality of Google’s SERPs. These advances inevitably require websites to adapt and improve as well, in order to keep up with the changes introduced by the algorithm and continue to ensure optimal online visibility.
Google Core Update and impact on search results
Whenever Google releases a core update, the effects on SERPs are not slow to be felt. One of the most crucial elements to consider is how the update can alter the position of websites in search results. This is a well-known phenomenon that leads to fluctuations, sometimes drastic, in a site’s ranking: some pages may see a surge in positions, while others may drop significantly.
However, it is crucial to understand that a core update is not designed to punish or reward specific sites: rather, it introduces new evaluation parameters that revise the importance of certain factors or attributes within the algorithm.
A site may lose positions not necessarily because it has suffered a direct penalty, but because Google has recalibrated its criteria and found other pages that better meet the new guidelines. In this dynamic, sites that have evolved and aligned better with the principles Google intends to throw to the forefront with the new algorithm may be favored. It is a constant reminder of the importance of maintaining a flexible, quality-driven SEO strategy. Sites that have hitherto dominated SERPs based on standard practices may suddenly find themselves at a disadvantage compared to emerging entities that have invested in content that is more comprehensive, authoritative or better optimized for today’s user needs.
The combined effect of the core update thus goes far beyond just rankings: it has a direct impact on organic traffic and, consequently, on a site’s visibility and profitability. Shocks in rankings can lead to a significant increase or decrease in visits, affect conversions and, finally, touch the economic sphere of a business. For this reason, no site can afford to ignore the signals and indications that come from a Google core update. Constant monitoring and adaptability become the key factors in reacting promptly to changes and establishing action plans that help maintain, and if possible, improve, a site’s position in the increasingly competitive universe of SERPs.
What are the effects of Google core updates on SEO and websites
When Google releases a core update, the changes that occur can be a real earthquake for a website’s SEO strategy. The effects of these core updates manifest themselves in multiple ways, profoundly affecting online visibility and how users interact with our content.
From an SEO perspective, a core update redefines the evaluation parameters that the algorithm uses to rank content. This means that the tactics and techniques that worked until yesterday may no longer be effective: therefore, even a site built respecting all the standard SEO rules may suffer a drop in ranking. This frustrating (and frequent) case happens because Google has reevaluated ranking factors, giving more weight to elements such as content quality, authority, user interaction, or relevance of answers to queries over structural or technical criteria. Constantly adapting to these changes in the algorithm is essential to not lose ground to competitors, and this is where the ability to understand these changes immediately comes into play so that timely action can be taken.
The influence of a Core Update is not just limited to a site’s organic traffic and ranking, because it is clear and undeniable that algorithmic changes have a direct impact on a website’s profitability: a decrease in organic traffic can mean a drop in sales, leads, site registrations, or any other KPI that measures online business success. These economic effects can propagate quickly, affecting not only online performance but also long-term strategic decisions. Faced with this scenario, it is crucial to approach each core update with the right attitude: not as a threat, but as an opportunity to improve. Listening carefully and monitoring emerging trends allows us to adapt and refine our SEO strategy, keeping the site aligned with what Google considers to be of the highest quality in the present moment.
How to monitor a Google Core Update
In this regard, if each core update can cause major changes in search results, it becomes a must-have practice to monitor these interventions, understanding in a timely manner how it may affect our site in a way that not only defends acquired rankings, but also seizes opportunities to advance further.
One of the primary tools for monitoring updates is the Google Search Status Dashboard, a simple information platform that reports all major “status” changes in search engine activity, promptly flagging the release of updates and work progress, paralleling what Google does through official social channels.
No less useful is the Google Search Console, which provides a wealth of valuable data for assessing the performance of our site, comparing organic traffic and keyword rankings before and after the update. The first sign of a likely impact is a significant change in the number of clicks, impressions and average keyword rankings.These metrics are crucial in highlighting whether the update is favoring or penalizing our website and gives us the opportunity to take swift action where necessary.
Of course, tools such as SEOZoom are also a valuable aid in getting a more detailed and specific view of ranking fluctuations, so we can closely follow keyword behavior and page performance to understand where we are feeling the effects the most. By broadening the analysis, we can also learn how a core update has affected the competition or the entire target industry, to gain the strategic advantage of taking precise action and anticipating competitors’ moves.
Monitoring becomes even more essential when signs of possible negative impact begin to appear. Here it is important not to panic and interpret the data correctly: core updates, as we have already mentioned, do not penalize specific sites but reassign new priorities based on new quality criteria. Our task is to identify precisely which elements of the algorithm have been recalibrated and how our site responds to these new inputs. Contextually, it is useful to follow official Google channels and keep an eye on discussions by industry experts on specialized forums and social platforms, so that we can also gather additional insights not apparent at first analysis.
Core Update: What to do if your site has been negatively impacted
Although Googlers are constantly trying to reassure SEOs and site owners with respect to the possible fluctuations caused by an update, it is clear nonetheless that the most natural human reaction, especially when there are declines for one’s own site, is to look for a solution to reverse course, which is why Google, too, has provided various guidance dedicated to sites affected by an update.
The premise is that “there may be nothing to fix” on the pages of the site, but more importantly that one should not “try to fix what is not broken” by focusing on the wrong areas.
Therefore, Google’s message is that there is “no miraculous intervention or fix” that can save pages, but only a set of useful guidelines to keep in mind and apply to any site that wants to compete on the search engine and do SEO, which can help keep its pages safer from search engine algorithm updates and prevent any jolts in SERPs.
Finding yourself with a significant drop in traffic and ranking following a Google core update can be destabilizing. But if we find ourselves in this situation, it is critical to react with pragmatism and determination. The first step is a thorough site assessment: we need to put under scrutiny not only the numbers, but more importantly the overall quality of what we are offering users. This process of analysis must start with the basics, specifically considering the content within the site. Are we providing valuable, up-to-date and relevant information? Is our content truly responding to the queries and needs of the target audience? In many cases, an algorithm update signals a need for improvement in the clarity, depth or accuracy of the information offered.
Another area that deserves attention isuser experience. A site that is easy to navigate, fast loading, and optimized for mobile devices is less likely to suffer from penalties. Paying special attention to site speed, internal link structure, and ease of access to the most relevant information is essential. Google rewards sites that offer intuitive and unhindered content fruition. In other words, ensuring that the site not only attracts visitors but provides them with a positive experience is crucial to maintaining a good position in the SERPs.
After performing a comprehensive analysis, the next step is to apply corrective actions where necessary. This could mean rewriting or updating outdated content, improving the quality of sources used or implementing more advanced SEO practices to align with Google’s new parameters. In some cases, it may be appropriate to take a step back and completely rethink the approach to content creation, perhaps introducing content marketing strategies that better enhance relevance and authority.
A key word in this phase is “patience”- recovery after a negative impact from a core update often takes time. Contrary to popular belief, results are not immediate, even if an adjustment strategy is adopted quickly. Google needs to collect, evaluate and process the changes made to the site in line with the new criteria. Therefore, constantly monitoring the results and making any further adjustments will be crucial to get back on a positive trajectory, again consolidating one’s place within the SERPs. Usually, it is considered necessary to wait at least a couple of weeks to see improvements, or even the release of a new core update.
How to react to a Google update
Broad core updates are thus designed to ensure that, overall, the search engine effectively follows through on its goals of presenting relevant and authoritative content to users, and in their release period they produce effects on SERPs that are also notable, with sites that may notice drops or gains.
According to Google, “there is nothing wrong with pages that may perform less well after a core update”: drops after an update are not dependent on violations of Google’s webmaster guidelines nor are they to manual (called manual actions) or algorithmic penalties, because a core update is not intended to affect specific pages or sites. Instead, the changes are about improving the way Google’s systems evaluate content in general and “may make some pages that were previously undervalued perform better.”
Either way, if SEO tools show us a drop in rankings for many pages and we suspect it may be related to the timing of a major update-and if Analytics confirms the drop-Google recommends using Search Console to determine if a change needs to be made.
The work consists of four steps:
- Checkwhether the core update has been completed by checking the Search Status Dashboard for the start and end date of the broad core update. It is not advisable to take action during “release progress,” because sometimes fluctuations are temporary.
- Compare the right dates. More specifically, Google suggests waiting at least a full week after the completion of a broad core update before analyzing the site in Search Console. At this point, we need to compare the completed week’s returns with those of the week before the main update was distributed, to better identify what exactly changed.
- Examine the main pages and queries, evaluating how they ranked before and after the main update to see if the drop is small or large. In the case of a small drop in position (e.g., from position 2 to 4), there is no need to take drastic measures: rather, Google advises avoiding making changes to content that is already performing well. If the drop in position is sharp (e.g., from position 4 to 29), a more thorough evaluation is needed, not just looking at individual pages, but analyzing the site as a whole.
- Analyze the different types of search separately, to understand whether the noticed drop occurred in Web Search, Google Images, Video mode, or the News tab.
Evaluate your own content
Basically, the guide invites us to pay attention to a hot topic for everyone working online, which is the creation of effective text and content. When faced with a decline, it is normal to react by trying to “do something,” and the advice that comes is to first check whether the site offers the best possible content, because “that’s what the algorithms are trying to reward.”
In addition to pointers to try to create content that is useful, trustworthy, and designed for people-in light of the crackdown introduced by Google in late 2022 around this topic-another possible starting point for figuring out if the direction is right are Google’s “old” 23 questions for building quality sites, reinterpreted in light of the changes that have taken place in recent years and divided into four categories: “content and quality,” ‘experience’ and expertise (the Experience and Expertise of the EEAT paradigm), ‘presentation and production’ ( writing well), and finally ‘comparison,’ or doing competitor analysis and comparisons with those ahead of us in SERPs.
- Issues on content and quality
- Does the content provide original information, reports, research, or analysis?
- Does the content provide a substantial, complete and comprehensive description of the topic?
- Does the content provide in-depth analysis or interesting information that goes beyond the obvious?
- If the content is based on other sources, does it simply avoid copying or rewriting articles and instead provide substantial added value and originality?
- Does the title and/or H1 of the page provide a descriptive and useful summary of the content?
- Does the title and/or H1 of the page avoid being exaggerated or shocking?
- Is this the type of page you would like to bookmark, share with a friend, or recommend?
- Would you expect to see this content on or referenced from a print magazine, encyclopedia, or book?
- Questions about experience and expertise
- Does the content present the information in a trustworthy way, such as with clear references to sources, evidence of the expertise involved, information about the author or the site that publishes it (e.g., with links to an author’s page or About page on a site)?
- If you research the site that published the content, do you get the impression that it is well trusted or widely recognized as an authority on its topic?
- Was this content written by an expert or enthusiast who demonstrates knowledge of the topic?
- Is the content free of easily verifiable factual errors?
- Would you feel comfortable trusting this content on matters related to your money or your life?
- Questions about presentation and production
- Is the content free of spelling errors or stylistic problems?
- Is the content well written or does it look sloppy or rushed?
- Is the content mass-produced, outsourced to a large number of creators, or spread over a wide network of sites so that individual pages or sites do not receive the same attention or care?
- Does the content contain an excessive number of ads that distract or interfere with the main content?
- Does the content display well for mobile devices?
- Comparison issues.
- Does the content provide substantial value compared to other pages in search results?
- Does the content appear to serve the genuine interests of site visitors or does it seem to exist only to try to rank well in search engines?
In addition to answering these questions ourselves on our site, Google invites us to request “honest evaluations from others we trust who are not affiliated with the site.” Studying traffic and keyword declines, then, may require an audit that identifies which pages have been most affected and which types of searches, carefully analyzing the results to see how they are being evaluated against what was written before.
The other sources of information for trying to have well-performing sites regardless of updates are Google’s quality rater guidelines, remembering (again) that the information provided by raters is not used directly in the ranking algorithms, but serves as a useful indication, much as “a restaurant does with customer feedback,” of whether systems are working and performing well.
That said, understanding how raters learn to evaluate good content could help improve a site’s content and, potentially, achieve improvements in search engine rankings.
Google update: the way to catch up is to improve content
And so, Google’s guidance certainly gives us a good guide to try to react to the consequences of a major update and an invitation not to panic: the main advice is just that, which is not to try to make substantial interventions in the immediate term, to disrupt the site for declines brought about by updates, because fluctuations can be continuous and there is no certainty of recovering lost traffic anyway.
Better then to think about the bigger picture, check the site’s content and make sure it meets Google’s quality requirements, and try to improve it if necessary. With the understanding, however, that sometimes it may not even take any action at all to move up in the rankings, if Google (with a new update) comes back to consider that page worthy of attention and favor.
Specifically, there are (at least) three things to keep in mind when making changes as a result of an update:
- Avoid making “quick” changes(such as removing a page element because we read/heard it was bad for SEO), focusing instead on making changes that make sense for our users and are sustainable in the long run.
- Consider how to improve content in meaningful ways.For example, it might be that rewriting or restructuring content makes it easier for the audience to read and navigate the page.
- Deleting content is a last resort,and should be considered only if we think the content cannot be recovered. In fact, if we are considering deleting entire sections of the site, it is likely a sign that those sections were created first for search engines, and not for people. If this is the case we find ourselves in, then eliminating unhelpful content can help good content on the site perform better.
Timing for recovering from slumps after updates
Google’s latest advice concerns the recovery and optimization work that can be done on the site, and in particular the answer to the frequently asked question, “How long does it take to recover if I improve the content?”
Broad core updates tend to be rolled out several times throughout the year, and so a piece of content that has suffered a negative backlash from one update (and makes the right improvements) may not recover until the next update.
However, Google is constantly working on search algorithm updates, making even smaller core updates that are not publicly announced because they are “generally not very noticeable”; however, when they are released they can result in recovery for sites that have made valid optimizations.
Thus, according to the official guidance, it takes time to see an effect in search results after making improvements: some changes may have a positive impact in a few days, but it may take several months for Google’s systems to learn and confirm that the site as a whole is now producing useful, reliable, people-centered content over the long term. If it has been several months and we have yet to see any effect, it may mean waiting until the next major update.
It is important to note that “improvements made by site owners are not a guarantee of recovery, nor do pages have a static or guaranteed position in Google’s search results,” because only the rule that “more worthy content will continue to rank well on our systems” applies.
Another important clarification relates to the way the search engine works, because “Google does not understand content the way humans do,” and so it looks for signals about content and tries to understand how these relate to the way humans evaluate relevance. “The way pages link together is one well-known signal we use,” Google admits, ”but we use many others that we don’t disclose to help protect the integrity of our results.”
Google Update, tips for recovering rankings and traffic
Further practical advice and insights for recovering from a collapse resulting from an update have also come over time from other Googlers, and in particular from theubiquitous John Mueller, who during a YouTube Hangout responded to a user submitting the case of his site, which collapsed after a Google algorithmic update, asking in particular “how many months should I wait to see an upturn and recover” having started “working on quality content.”
Mueller immediately reiterates a concept that we have already addressed, namely that a core update is not penalization for particular sites or types of sites, and that when drops occur after updates it does not mean that Google’s algorithm “is saying that site is of bad quality.” Although the consequences are identical (loss of positions in SERPs and thus organic traffic), core updates and penalties are substantially different, and Google is keen to point this out.
Google assigns a penalty to a site after a violation of the Webmaster Guidelines, which is communicated through an alert via the Search Console. Declines after algorithmic updates, on the other hand, are part of “normal” fluctuations in SERPs and there are no notes or notices officially reporting them.
More importantly, a penalty is sanctioned after an error by the editor, a violation, or behavior that does not meet Google’s standards (spam content or unnatural links, for example), while instead the drop resulting from updates just means that the search engine has reworked its rankings and decided that other sites offer better answers to users.
With updates, Google refines its results and answers
John Mueller makes it clear: the reason sites lose rankings is that Google’s new algorithm has decided that some sites are more relevant. Basically, with updates Google evolves its ranking system based on new criteria, which are used to determine which pages are more relevant to the queries.
So it’s not about finding fault or a problem in the collapsed site, “it’s not about doing something wrong” and fixing it (and then, the Search Advocate adds, “communicating it to Google, which acknowledges the correction and returns the site to its previous position”), but rather a reworking of the search engine’s own analysis and calculations. In practice, Google determines that those pages are no longer as relevant and relevant as it originally thought, and such changes can occur several times over time.
Core update, what to do when the site loses traffic and ranking
Further input on the topic also comes from Roger Montti on Search Engine Journal, who in a guide to “core alghorithm update recovery” addresses the characteristics of Google broad core updates, saying that in his experience one can recognize at least two broad categories of losses after algorithmic updates.
The first case is the simple drop in rankings for certain queries: it happens when Google decides to reward certain sites by elevating their positions in SERPs, consequently causing a drop in pages previously ranked high in the search engine’s rankings. Then there are complex situations, when a site completely loses its rankings, which are indications of broader problems that need to be addressed with a complete project optimization.
The time required to recover
The type of criticality obviously depends on the time it takes to recover, although there is good news coming from John Mueller: Google’s algorithm is constantly being updated, and any improvements made to web pages can yield results already in the short to medium term, without having to wait for the next broad core update.
Specifically, the Googler premises that “on the one hand we have the broad core updates, which are sort of big changes in our algorithm, and on the other hand we have a lot of little things that keep changing over time. The whole Internet is constantly evolving, and so Google’s search results change substantially from day to day and similarly can improve from day to day.”
Therefore, when significant improvements are made to a website negatively affected by an update it might be possible “within some time to see these kinds of subtle changes, because it’s not a matter of waiting for a specific update to see the effects of the interventions.”
A drop after updates does not mean the site is bad
In concluding his response, Mueller however reassures: losing rankings after an update does not mean that there is something wrong (bad is the adjective he uses) with the site, because such maneuvers are more general and do not target specific sites.
Where to take action to recover rankings
Despite the premises and recommendations, however, let’s face it: if our site collapses after a broad core update we want to roll up our sleeves and try to turn it around as quickly as possible!
Actually, you have some more or less complex interventions that we can try to implement in quick response to remedy the ranking collapse: we can, for example, start working on optimizing page content, updating or refreshing it, or check technical aspects, such as user experience, speed or general and mobile performance.
In addition, given John’s insistence on the term “relevance” (which we generally translate as relevance or relevance), it is good to try to check how the site responds to this criterion, studying the new SERPs and especially trying to investigate the competitors and pages that have benefited from a rise in ranking, so as to understand what content best responds for Google to the search intent of the query, which is ultimately the final reference of our work, the key with which Google tries to ensure that the user satisfactorily concludes his path on the search engine.
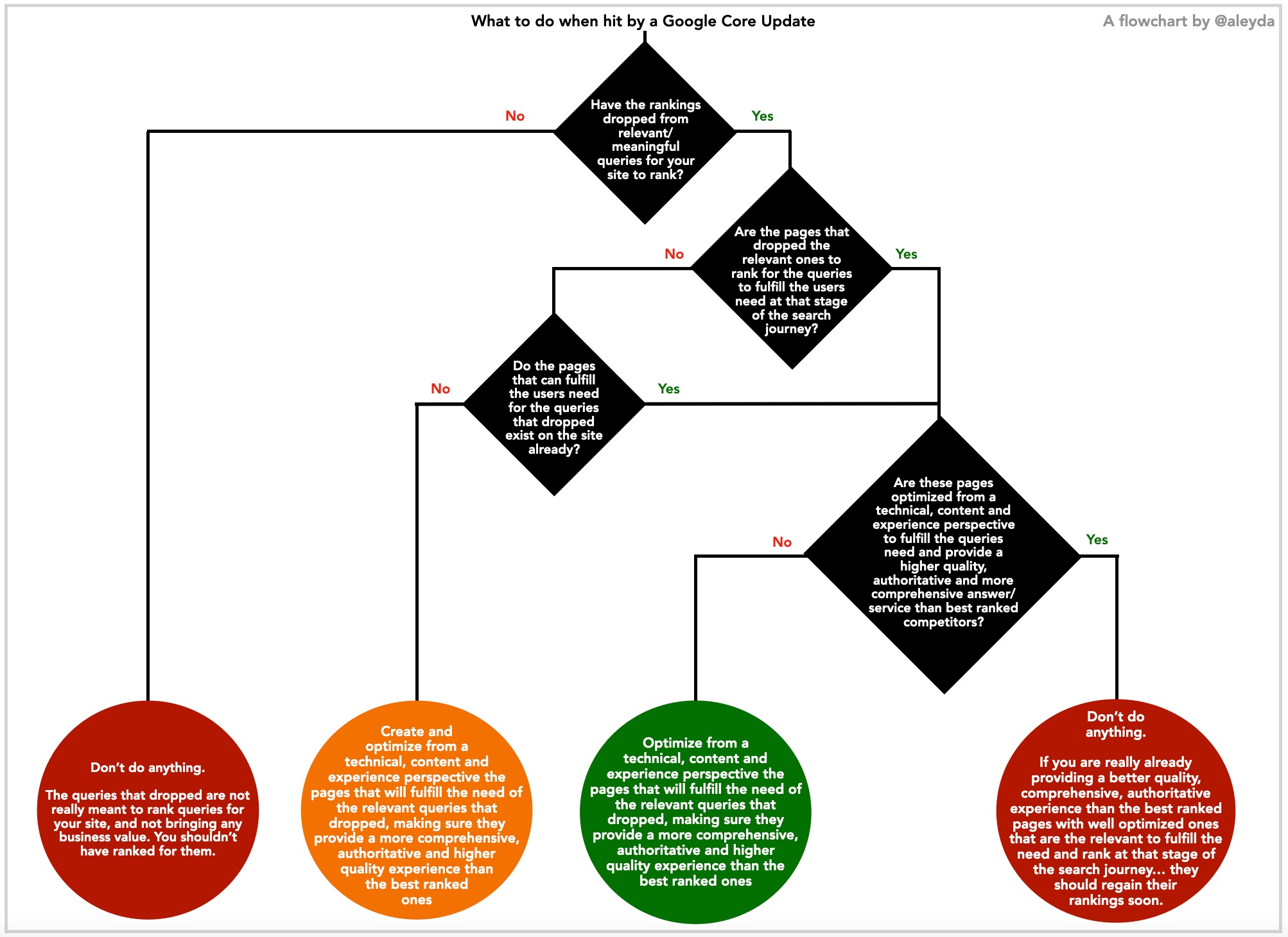
Ultimately, in order to understand what to do if our site has been hit by a Google Core Update we can refer to this scheme devised by Aleyda Solis , which takes us down the path that is closest to our experience and our specific case!
What Google’s major updates are for
But why does Google release these updates periodically, specifically?
According to an interesting insight by Ryan Jones, with broad core updates Google changes the weight and importance of certain ranking factors, more or less noticeably on SERPs and without (of course) there being any further public details (so as not to reveal algorithm secrets ). Returning to the search engine’s official guidance, Danny Sullivan told us that the choice to announce and confirm the release of the core updates stems precisely from the fact that they generally “ have a noteworthy impact and, during their implementation, performance drops or improvements may occur for some sites.”
Since they are not intended to improve specific areas of Search, but are in fact general and broad, broad core updates serve to improve search results globally and-an expression used when one such update was released-to benefit pages that were “previously undervalued,” something that is important to keep in mind with a view to optimization and recovery for affected sites.
In addition, several analysts have noted an (indirect) link between Core Update and the work of quality raters, or rather with the guidelines for quality raters (and their various updates). It is still Jones to speculate, for example, that the release of the update could be the culmination of a complex process, which begins with the execution of a new training set through Google’s machine learning ranking model, goes precisely through the application of this new set by the quality raters (who identify the most relevant result sets based on the new criteria), and ends with changes to the generation of results. This is not to imply a direct relationship between quality raters and rankings, however, because we know that the work of these external contributors is limited to evaluating the relevance of the results to the query and the quality of the answers to the instructions given to them, and thus not to evaluating the site relative to others.
The relationship between core updates and other updates
Again to clarify the context, it is important to understand that broad core updates represent only a tiny fraction (typically there are two or at most three per year) of the thousands of changes Google makes to its core algorithm each year.
For example, in 2020 Google made 4,500 changes to the Search system, with an average of more than 12 interventions per day, and the number is steadily increasing (in 2018 there were 3,200, in 2010 less than 500!); next to these, then, Google reported that it performed always in 2020 alone more than 600 thousand experiments, which as well can affect SERP ranking, traffic and visibility.
As early as a few years ago, Google’s Gary Illyes explained how most of Google’s algorithms and tweaks do not specifically target particular pages or topics, but “work in unison to generate ranking scores”: Illyes called them “baby alghoritm,” or little algorithms or algorithms, would be millions and look for signals in pages or content.
How the implementation of a broad core update works
Those who follow our blog should by now be familiar with the format by which the SEO community is notified of the launch of a broad core update, a standardized practice first initiated in March 2018 for the March 2018 broad core alghoritm update.
The first announcement comes a few hours before the release on Big G’s official channels (website or social), followed by the announcement of the official start of the update and, about 15 days later, the message that the roll-out has been completed; only sometimes, very infrequently, are (few) additional details shared during the release period.
Also standard by now is the name Google gives to the core algorithms, which follows a very simple Month+Year+Core Update pattern since the March 2019 Core Update, to “avoid confusion and simply and clearly say what kind of update it was and when it happened,” as Danny Sullivan clarified on the occasion.
Google’s choice to confirm broad core updates stems from the fact that they “typically produce some broadly noticeable effects,” meaning “some sites may notice declines or gains” over the course of the release. By clarifying the context, then, Google is giving a way for those experiencing such situations, and traffic drops in particular, to know what is happening and plan recovery actions-without disregarding Google’s guidance in this regard.
From a practical point of view, some major algorithm updates are implemented quickly, while others take up to 14 days for the rollout to end: their impact on SERPs is generally distributed, because they make themselves felt for several days along this timeframe (and sometimes even after) and not just exactly on the day an update is announced or confirmed, and this adds some complexity to data analysis – which is why it comes in handy to check tools such as our SERP Observatory, which keep a constant eye on search engine activity.
What is important, in fact, is to try to always keep track of what is happening in the “Google” context, because only in this way is it possible to intuit whether traffic declines are related precisely to the effects of a broad core update or whether they instead stem from different issues that need to be investigated more analytically-and for this reason, we have dedicated a section to Google’s major updates, which help keep track of ongoing activity in the Search ecosystem.
The difference between broad core updates and other major updates
Broad core updates are different, then, from Google’s other algorithmic updates, whether they are baby alghoritm or large updates that directly affect ranking, or rather a specific aspect of the search engine’s ranking system.
Many of the famous updates we hear about, from Penguin to Panda, Pigeon to Fred, and so on, were implemented to fix specific errors or problems in Google’s algorithms: for example, Penguin was to address link spam, while Google Panda improved the overall quality of Search and Pigeon addressed spam on local SEO. More recently, then, we can recall Page Experience, which introduced core web vitals among the ranking factors, or the Reviews System.
The characteristic of these types of updates is obvious: they have a specific purpose and address only one specific aspect of the algorithm. When providing information about it, Google explains what it is trying to achieve or prevent with the individual algorithm update, thus giving webmasters, site owners, and SEOs a way to possibly change strategies and misbehaviors to correct their pages.
On the contrary, broad core updates do not evaluate a single ranking factor, but the entire complex of the evaluation system (or at least a large portion of it), going so far as to definenew criteria for judging the quality of pages in relation to parameters such as user search intent, relevance, relevance, authoritativeness of the content offered (which always falls under EEAT parameters ), overall user experience, mobile experience, and so on.
For this very reason, it is difficult to isolate and determine precisely what the ranking declines found after a major Google update are due to, and indeed, according to the guidelines offered by the search engine itself, it is even “useless” to try to correct anything.
What we need to remember, basically, is that a broad core update is not a penalty or a sanction: a site that suffers a drop in ranking, traffic and visibility may not have done anything wrong and there may not be any corrections to be made.
It is the context around it that has changed, because Google has performed an update on its own search results, based on a new set of ranking “rules” that (while not designed to target specific pages or sites) can produce some noticeable changes to site performance-and all this without taking into account the natural fickleness of SERPs and rankings, which can also be affected by competitor activity and other variables such as seasonality, news or events affecting search, and more.