What to do when Google makes the wrong page of your site rank
It is a case that can occur frequently and that we can be surprised of: we work on the optimization of a page, we take care of various aspects and we think we have produced a content with good opportunities to position, but there are not real results. Even worse, looking at the SERP for the “goal keyword” we realize that Google not only snubbed that page, but ranked (and pretty well so) another page of our domain, which does not have the same effectiveness for our strategy. On what depends this situation of positioning the wrong page on Google and what can we do to correct this error?
The wrong page ranking on Google
This is a frustrating but common problem that occurs when – for some reason – Google does not recognize the page that we have envisioned as the best destination for traffic and user searches. With the display of the page “wrong” we expose ourselves to some strategic risks: the page positioned could be old, not optimized, could lead to fewer conversions or have high bounce frequencies.
Even if for us the content and the page we have built represents the “best answer” to a query, as we know in the SEO field the logic cannot always be applied and only the algorithms determine the ranking.
Fortunately, there are several steps and SEO techniques that can attempt to correct this problem and make Google understand what content we want to place.
Why does Google make the wrong (to us) page rank?
Before we dive into the correction and optimization operations, however, we should try to detect the issue and understand why Google chose a different page than the one we had thought of (and for which we worked).
We must try to diagnose the problem, remembering that the mission of the search engine is to provide users with the best pages for their requests: therefore, the algorithms have determined that the page we prefer does not possess sufficient quality and does not guarantee the maximum level of user satisfaction, so as not to deserve a high positioning.
Among the most frequent scenarios we can come across are the best positioning on Google of an old and outdated version of the homepage, the best ranking of a promotional page with an offer now obsolete instead of the one with the new proposal, SERP presence of service pages (such as those related to privacy and cookies), up to the cannibalization of keywords. In this case, the error arises upstream, because we have published content on identical topics (or deemed very similar) and therefore Google is in difficulty in evaluating the page to be placed.
If we believe that we have an already published page that is rich in content, optimized in every aspect and built after a keyword research targeted, but nevertheless was not taken into account by Google as the best response to the query user, we need to continue the analysis so to find the catch.
That is to say, trying to understand if the page that is more effective and specific for us for the topic than the wrong one is actually such also for the user (and for Google), study the data of public interaction to understand if it is engaging and attractive, if it is easy to read; and then, from a technical point of view, verify that there are no errors such as a block in robots.txt, presence of duplicate content, content actually optimized for specific keyword, with rich texts and not thin ones.
These are just some of the aspects to assess when we find that Google has placed the wrong page of our site, and after identifying (or perceived, at least) the causes of the problem and confusion we can move to corrective action.
What to do when Google makes the wrong page of our site rank
When we stumble into this situation, our goal is to try to improve one-page ranking signals for a specific keyword by fielding a number of predominantly onpage SEO optimizations, as also suggested by this article by Adam Heitzman on Search Engine Journal, and also taking advantage of the new tools contained in Seozoom.
The first task to be undertaken to correct the positioning of a wrong page is to evaluate the search intent that underlies the main keyword that we have identified (and that we have tried to intercept): today more than ever, Google tries to classify content that best responds to the user’s intent and that therefore satisfies the reason why that person did the search, and not understanding it means substantially wasting time and resources.
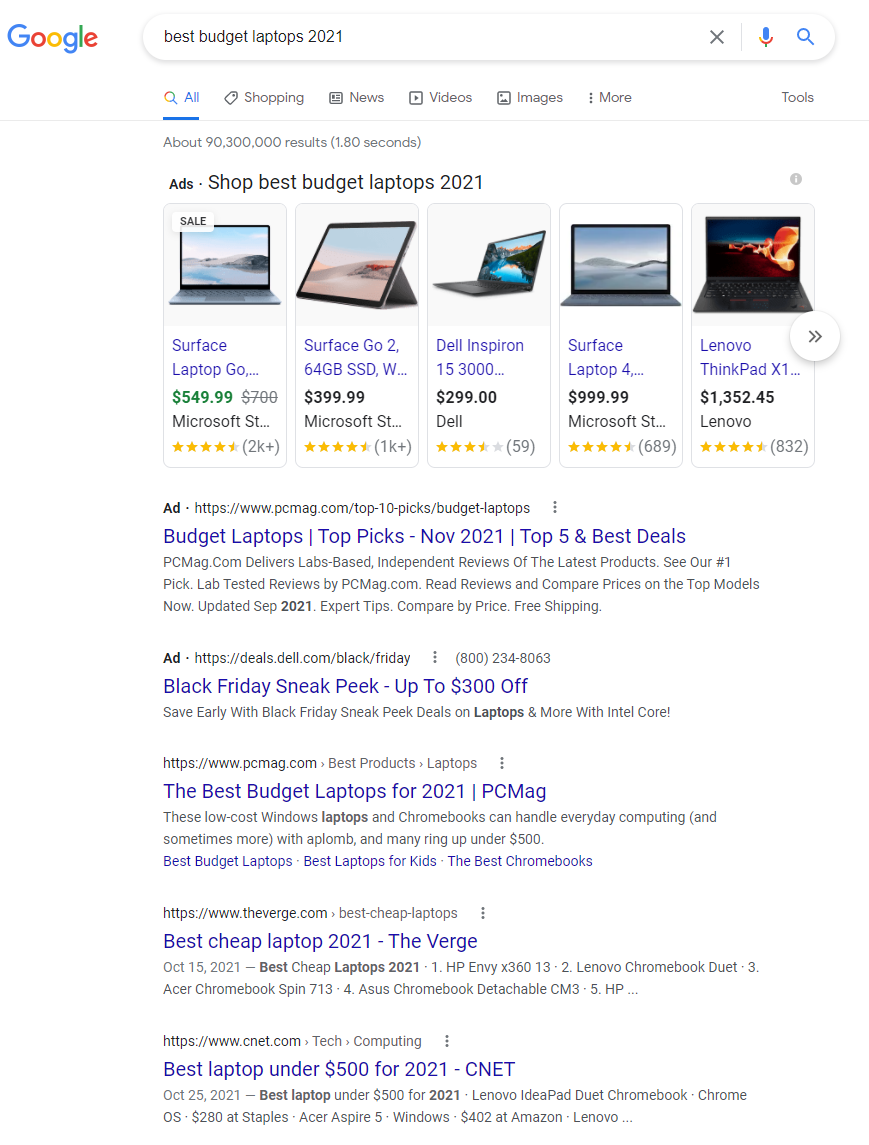
Therefore, by extremizing, if the search intent of that keyword is strictly transactional we do nto have many opportunities to position ourselves well with a page that offers informative content and vice versa, and as exemplifies the article by Heitzman “If your main keyword was best budget laptops 2021 and you wanted your product page or category page to rank for that, you probably don’t have a chance,” because that is what Google rewards and shows for that query:
The SERP (speaking of Google USA) is dominated by pages from “third-party aggregator sites and review sites listing a comparison of the best laptops”, and indeed “no manufacturer or retail site ranks on the first page for this query”. Therefore, from a strategic point of view you need to completely shift your attention from this keyword or take note of the situation and reorder the content and page of our site to align us with what Google intends to show.
Onpage optimizations to correct Google
After making sure that the content actually corresponds to the intent identified by the search engine, we must study the content of the page we hope to place, to understand if it is really relevant and optimized.
The American author suggests to try to answer some questions that define a basic idea of the onpage optimization of a content, such as:
- Is my main keyword in the page title?
- Do I refer to the main keyword in the description?
- Net of the myth of the word count, the length of the content is in line with that of the top 10 or the top 20 sites classified?
- Do competing sites use shared semantic keywords that I have to embed on my page?
- Does my page answer questions that a user might have to know more about this topic?
No less useful is to try to consolidate the page we want to improve by building an effective network of internal links from pages with high authority that are relevant to the topic, in which to add a link to the destination URL using possibly also an aggressive anchor text.
A weight to the authority of the page is also represented by external links: if the page incorrectly positioned by Google receives backlinks from other sites, we can contact them to ask them to point to the page that we want to see in SERP, which could then acquire new value in the eyes of algorithms.
As mentioned, then, the data on user behavior offer us valid insights to understand the actual level of satisfaction of the page: among the parameters to be observed on Analytics there are the bounce rate, the percentage of clicks and, where applicable, the conversion rate. If what we call the relevant page still gets traffic, but people land and leave quickly, it means that the content does not interest users, that they do not find what they expected or that they cannot positively navigate.
Techniques to make the wrong page lose rankings
After trying to improve the conditions of the page we are trying to bring up some Serps we must then focus on the downgrade of the page that is currently classified for that search term.
This is something that goes against virtually all SEO teachings, but, Heitzman also explains, “it’s what needs to happen to ensure that the relevant page is able to position itself”.
An immediate method to achieve the goal is to change the content of the page not relevant, removing all traces of the keyword and its terms, continuing with a remodeling of internal links, so that they point away from this page and towards the correct page, and then repeating the same operation to the external links, contacting the sites that host backlinks to this page to request a redirection to the correct resource.
Redirect 301, the final resource to correct the ranking of two pages
If the roads just described do not lead to the expected results within a reasonable period of time – remember that the SEO needs time to work! – There is still a way we can go: set up a redirect 301, physically eliminating the wrong page to bring Google to the right resource that we want to place.
This redirection will signal to Google the permanent move of the old page to a new location, and allows (usually) to transfer any equity of the old page to the new page, thus offering it a boost in terms of ranking.
How to analyze the problem with SEOZoom
A concrete support in this activity of identifying a possible conflict between pages and better positioning than the wrong one, as well as in the correction of problems emerged, offers the renewed SEOZoom 2.0 suite.
At the moment, in fact, our tool is the only one in the world to use an engine able to perform a complete SEO analysis in real time, which is not limited to trivializing the tags of a web page, but examines all the web pages of competitor sites in real time, identifies the Search Intent of the users, evaluates Intent Match scores for the study page and for those of the competitors and provides a series of practical tips to optimize the work.
In particular, Seozoom does not only offer static information on the type of search intent identified for the keyword target – that is whether it is commercial, informational, navigational or transactional – but also shows the search intent “understood” by Google, immediately indicating the topics and keywords for which you can place a content, providing reliable insights always updated per second, tracing maniacally the intentions of search users in all sections of the Suite.
This allows us to improve more easily the content that is not positioned well, perhaps also using another innovative tool to enrich the information: for each keyword, in fact, Now are available the frequently asked questions of users that appear on Google, ideal for those who try to expand the topic of the text remaining in focus with what the search engine is positioning.
Very useful are also the features that allow you to discover the presence of a possible cannibalization between two or more pages of our site, as well as those that study the optimization of snippets by competitors better positioned to offer guidance on the format liked by Google, and even more the new function for monitoring the keyword of a project: now we can also change the URL identified by Seozoom automatically (based on the assessments of Google’s algorithms) and then actually understand what is missing from that page to compete for the keyword it was originally builded for.
SEO can correct Google
With these interventions we should be able to correct the ranking of “wrong” pages – that is, displaying in SERP in prominent positions of unwanted pages for a target keyword – and solve a problem that can have a negative influence on the user experience.
It usually takes simple steps to give the right signals to Google and move traffic to the desired page, with the end result of offering a better experience to the user, because the visits actually reach the right destination, to the benefit of engagement metrics.